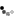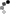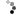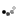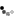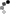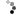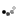|
LOTE 19:
THREE PILASTER CAPITALS
|
|






|
Preço inicial:
€
9 000
Preço estimado :
€14 000 - €16 000
Comissão da leiloeira: 18%
Mais detalhes
IVA: 21%
Sobre a comissão apenas
|
Three Pilaster Capitals
Gandhara, Pakistan
2nd century AD
Shale
Between 31.5 and 37 cm in length and 16 cm in height
CONSERVATION: Good general state of conservation, without restorations. Some slight bumps on the upper corners and on the outstretched forearms of the human figures.
Description
Set formed by three pilaster capitals with a clear Gandharan artistic style that shows the originality of framing, as a canopy, the male figures carved in high relief in its central part, by acanthus leaves and vegetal and floral decoration.
The central figures, unless they represented the Buddha, tended to represent either Bodhisattvas (followers of Buddhism who have devoted their lives and beings to attaining spiritual enlightenment) or the rich patterns of the artist himself who had been commissioned to execute the works. capitals. In the present case, this last option is the most plausible, since the figures, due to their attire, seem to represent subjects of a certain social and economic position, showing an attitude of offering respect (as in the case of the upper and lower capitals) or holding the hands an object or animal (case of the intermediate capital).
These capitals derive from the classic Corinthian style, to which the figures of Buddha, Bodhisattvas or notable figures are incorporated, generally as central figures surrounded, and often shaded, by luxurious vegetal foliage. The representation of figures within the foliage of the Corinthian capitals is not in itself an Eastern development. From an early period, in the Mediterranean, in the ancient Greek world figurative additions are very common, taking the form of heads or busts.
This practice of architectural sculpture was not limited to the Gandharan culture and found favor in various areas of Central Asia, most notably India, where numerous examples were produced, named Indo-Corinthian capitals, which had the same iconographic scheme, albeit with stylistic variations.
The Greek Corinthian order is recognized by its appearance of an inverted bell, or basket, from which acanthus leaves overflow, whose stems give rise to a kind of volutes or spirals at the four corners.
The historical region of Gandhara, which corresponds to southeastern present-day Afghanistan, central and northern Pakistan, and northwestern India (including most of Kashmir), was a satrapy of the Persian Empire of the Achaemenids from the 6th century BC. Conquered by Alexander the Great, at his death it became part of the Hellenistic kingdom of Bactria or the Indo-Greek Kingdom, always weak and in continuous conflict until its disappearance by annexation to the Kushana Empire, at the beginning of the 1st century AD. The Kushans adopted many elements of Hellenistic culture, even applying the Greek alphabet to their language. Some authors prefer to speak in general of Kushana art or Eastern Hellenistic art, but the Buddhist theme is so decisive that its presence in the defining title of this school is necessary: Greco-Buddhic style of Gandhara.
Greco-Buddhist or Greco-Buddhist art developed over a period of about 1,000 years in Central Asia, from the conquests of Alexander the Great in the 4th century BC to the conquests of the Muslims in the 7th century AD. The name "Gandhara style" derives from the region of the same name, as it is the best known place of expression and is the artistic manifestation that arises from the cultural syncretism between the culture of Classical Greece and Buddhism, between Eastern and Western traditions. This curious and remarkable art is characterized by the strongly idealized realism of Hellenistic art—depictions of their gods in human form—and the earliest depictions of the Buddha in human form, which helped define the artistic, particularly sculptural, canon for art. Buddhist throughout Asia to the present.
The production of this eclectic sculpture and architectural decoration of Gandhara was always carried out in noble materials, in general hard stones such as porphyry, schist or basalt, occasionally decorated with metal inlays and precious gems, or stuccoed and polychromed if the material did not offer the perfection required by such a noble theme. The spread of the Buddhist cult was coupled with the prestige of the Kushana power.
Later, the area also had direct relations with the Roman world through trade and cultural exchange that developed through the Silk Road, which helped the survival of the adopted Greek artistic canons. Thus, Roman coins and sculptures arrived in Gandhara in which emperors, high dignitaries and gods appeared. The Greco-Latin influence in this region was key in its artistic development, both for the formal aspects and for the fact that Buddha was represented in human form. Gandhara will be the first center, along with Mathura, where not only Sakyamuni or the historical Buddha, but also other figures of the Buddhist pantheon, are personified in human form. This figurative representation will also favor the expansion of Buddhism throughout East Asia.
BIBLIOGRAPHY:
BEGUIN, Gilles. Buddhist Art. An Historical and Cultural Journey. RiverBooks. Thailand, Bangkok. 2009. pgs. 205 – 225.
BEHRENDT, Kurt A. The Art of Gandhara in the Metropolitan Museum of Art. New York. 2007.
BUSSAGLI, Mario. L'Art du Gandhara. Librairie générale française. Paris. nineteen ninety six.
ERRINGTON, Elizabeth; CRIBB, Joe; CLARINGBULL, Maggie. The Crossroads of Asia: Transformation in Image and Symbol in Art of Ancient Afghanistan and Pakistan. Cambridge: Ancient India and Iran Trust. 1992.
KURITA, Isao. Gandharan Art: The Buddha's Life Story & The World of the Buddha. (2 Vol.). Tokyo.
Provenance: Bought from Spanish private collection. O.C. Before from Gallery.
The piece includes a certificate of authenticity. If the piece is exported outside Spain, the seller will process an export licence. This process can take between 1 and 2 months. Shipped with insurance.